Ceramic Industry

Structural Ceramics:
Industrial alumina powder is an important raw material for manufacturing structural ceramics. α-alumina, calcined at high temperatures, is widely used in the production of mechanical parts such as ceramic tools, ceramic bearings, etc., due to its high hardness and excellent wear resistance. For example, ceramic tools maintain good cutting performance during machining, with hardness reaching 90-95 HRA. Compared to traditional metal tools, they offer higher cutting speeds and longer service life.
It is also used in the production of automotive engine parts, such as spark plugs and valves. The alumina ceramic insulator in spark plugs can withstand high temperatures and pressures, ensuring the normal ignition of the spark plug during engine operation.
Functional Ceramics:
In the field of electronic ceramics, alumina powder is used to manufacture components such as capacitors and sensors. For instance, multilayer ceramic capacitors (MLCC) are widely used in electronic devices. Alumina is employed as a dielectric material. Its high dielectric constant and low loss characteristics help enhance the performance of capacitors and enable electronic devices to operate more stably.
In piezoelectric ceramics, the proper doping of alumina can improve the piezoelectric properties of the ceramics, making them suitable for use in manufacturing ultrasonic transducers, pressure sensors, and more. These sensors play a crucial role in industrial detection, medical ultrasonic equipment, and other applications.
Refractory Field

Industrial alumina powder is a key component in advanced refractory materials. Due to its high melting point (2054°C) and excellent chemical stability, it is used to manufacture linings for high-temperature industrial equipment, such as steelmaking furnaces and glass melting furnaces. During the steelmaking process, the furnace lining must withstand the erosion and scouring from high-temperature molten steel. Alumina refractory materials effectively protect the furnace body and extend the equipment’s service life.
It is also used to produce refractory products such as refractory bricks and castables. The alumina content in refractory bricks varies, allowing them to adapt to the working temperature and environmental requirements of different industrial furnaces. For example, high-alumina refractory bricks (with an alumina content greater than 75%) can be used in metallurgical furnaces with higher temperatures, while medium-alumina refractory bricks (with an alumina content between 48% and 75%) are suitable for industrial furnaces with slightly lower temperatures.
Abrasives and Grinding Tools Industry
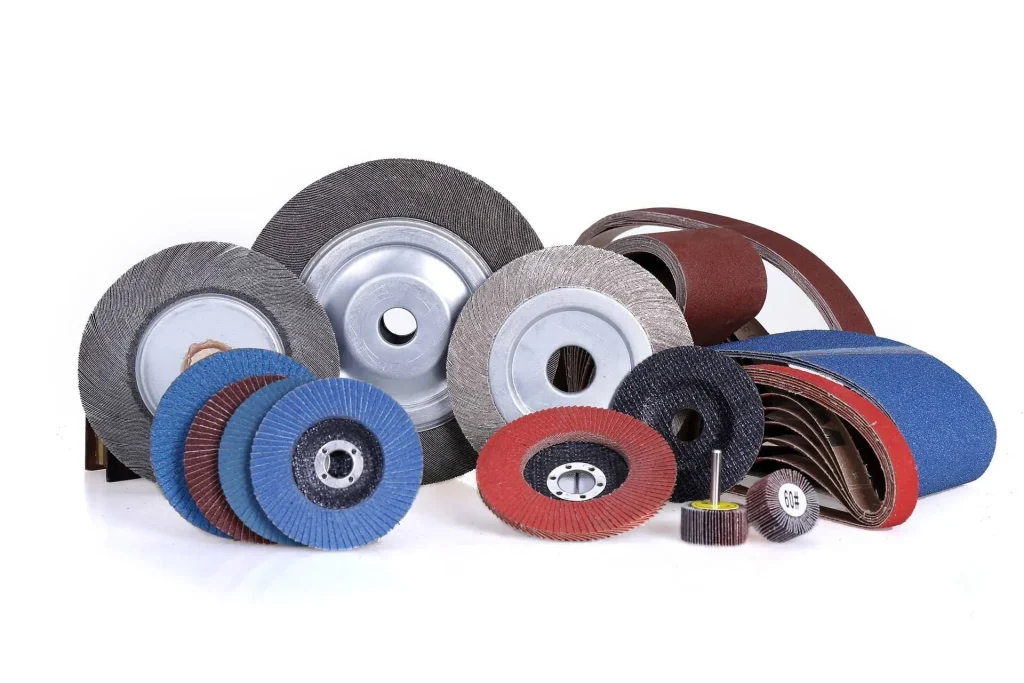

Alumina powder is one of the main raw materials for manufacturing abrasives. White fused alumina abrasive, whose hardness is second only to diamond, is used for precision grinding and polishing. For example, in the grinding process of optical lenses, alumina abrasives can achieve a high degree of flatness and finish on the surface of the lens, meeting the requirements of optical equipment.
It is also used to produce grinding tools such as grinding wheels and abrasive belts. In metal processing, alumina grinding wheels effectively remove excess material from the surface of metal objects and improve processing accuracy. For instance, when grinding automotive parts, alumina grinding wheels can quickly process various metal materials while ensuring the quality of the finished surface.

Alumina Powder